The COVID-19 global pandemic has resulted in an abundance of quick research follows an outbreak. In just a few months, more than a thousand studies on this topic have appeared in the scientific literature.
In this brief review, we analyze the bibliometric aspects of this study at the macro level, as well as those dealing with coronavirus in general. In addition, through analysis of the scope of the literature on COVID-19, we identify the dimensions associated with the main safety that these studies have so far dealt with.
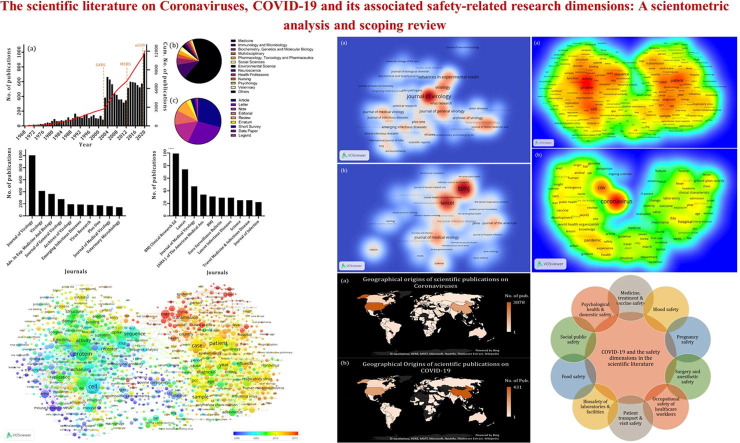
Our findings show that in various domains of research, and in spite of the medical aspects and clinical safety of vaccines and treatments, issues related to transport safety of patients, safety of health professionals, biosafety laboratories and facilities, social security, food security, and especially mental / psychological health and safety in the country have so far attracted the most attention from the scientific community in relation to the 19th COVID pandemic.
Our analysis also revealed a variety of potentially significant safety problems caused by global health emergency that now has attracted scientific attention only limited but may require more attention. This includes things such as cyber security, economic security, and the security of the supply chain.
These findings highlight why, from the perspective of academic research, interdisciplinary approach is holistic and collective scientific efforts needed to help understand and mitigate the effects of this crisis are safety implications reach far beyond bio-medical risk. holistic scientific understanding of salvation as COVID-19, the next crisis could be an instrument to be better prepared for a pandemic in the future.
Ten simple rules for running a successful women-in-STEM organization on an academic campus.
Academic culture faced by women in science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) in the United States has triggered the formation of groups of grassroots advocacy to empower women scientists in training.
However, the impact of these initiatives often measured and underappreciated. Our Women in Science and Engineering organization (WiSE) function postdoctoral researchers, graduate students and research technicians (trainee) in a private research institute for biological sciences.
Here we propose the following guidelines to foster women-in-STEM-focused groups based on a survey of our own scientific community as well as the experience of our group leader WiSE success. We hope these recommendations can provide guidance to the advocacy group in research and other academic organizations who want to strengthen their efforts.
While our own group is specifically focused on the country represented women in science, we hope this guide can be adapted and applied to groups that advocate for minorities in the scientific community that is larger (ie, those of gender, race / ethnicity, background socio- economic, sexual orientation, etc.).
